Gas Constant of Air in English Units
Values of R Gas Constant Value Units VPT 1n1 8314 462175 J K1 mol1 5189 1019 eV K1 mol1 0082 057 4614 L atm K1 mol1 1985 877534 cal K1 mol1 1985 877534 103 kcal K1 mol1 8314 462175 107 erg K1 mol1 8314 462175 L kPa K1 mol1. The gas constant is inversely used in diverse disciplines.
Air Composition And Molecular Weight
PV nRT when the variables are expressed in other units.
. General gas constant is R 831 J K-1 mol-1. The gas constant also known as the molar universal or ideal gas constant denoted by the symbol R or R is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. Each gas multiplied by the molecular weight of that particular gas.
Ideal-gas specific heats of various common gases a At 80F Gas constant Rc p c v Gas Formula BtulbmR BtulbmR BtulbmR k Air 006855 0240 0171 1400 Argon Ar 004971 01253 00756 1667 Butane C 4H 10 003424 0415 0381 109 Carbon dioxide CO 2 004513 0203 0158 1285 Carbon monoxide CO 007090 0249 0178 1399 Ethane C 2H. Specific gas constant for water vapor. It is denoted as R.
Universal gas constant R u 831451 J mol K 198589 Btu mol R. For air one mole is 2897 g 002897 kg so we can do a unit conversion from moles to kilograms. Temperature in degrees Celsius C.
Hence it is expressed in many units. These include the most commonly used values for the universal gas constant when working in metric units SI units English engineering units and US customary units. FtlbfslugR or m 2 Ks R e.
8314 1 002897 287 This means that for air you can use the value R 287 JkgK. The dimension of the gas constant is expressed in energy per unit mole per unit temperature. The origin of the symbol R for the ideal gas constant is still obscure.
These tables contain 188 values for the Universal Gas Constant in the most likely combinations of units. Mmixture ΣxiMi x1M1 xnMn 4 where xi mole fractions of each gasMi the molar mass of each gas The Universal Gas Constant - Ru - in alternative Units atmcm3molK. Specific gas constant for air.
Temperature R or K. The same regardless of the gas being considered. The following conversion factors for pressure units were used in generating the table.
Gas Formula BtulbmkR BtulbmR BtulbmR Air 006855 0240 0171 1400 Argon Ar 004971 01253 00756 1667 Butane C 4H 10003424 0415 0381 109 Carbon dioxide CO 2004513 0203 0158 1285 Carbon monoxide CO 007090 0249 0178 1399 Ethane C 2H 6006616 0427 0361 1183 Ethylene C 2H. The quantity of heat required to convert a unit of liquid at a specific temperature into its vapor at the same temperatureThe value of this quantity is usually given at the normal boiling point of the liquid and is measured in kJkg or. Ft 2 or m 2.
Defines a specific gas constant with a value of 287. R u universal gas constant Jmol K lb f ft lb mol o R 83145 Jmol K 008206 L atmmol K 6237 L torr mol K T absolute temperature K o R For a given quantity of gas both n and R u are constant and Equation 1 can be modified to p 1 V 1 T 1 p 2 V 2 T 2 2. 1 atm 101325 Pa 1 psi 6894757 Pa 1 torr mmHg 133322 Pa at 0C 1 in Hg 338638.
R 8314 JmolK. We usually model air as a uniform no variation or fluctuation gas with properties that are averaged from all the individual components. Universal gas constant and ideal gas law The universal gas constant Ru is as its name implies universal ie the same regardless of the gas being.
Heat of vaporization L v. The value of R depends on the units involved but is usually stated with SI. FtlbfslugR or m 2 Ks S.
PROPERTY TABLES AND UNITS 3 TABLE A-2UNIVERSAL GAS CONSTANT FOR DIFFERENT UNITS Pressure Unit Volume Unit Temperature Unit Mass mole Unit Gas Constant R psia ft3 R lbm 107315 psia cm3 R lbm 303880 psia cm3 Rg66994 bar ft3 R lbm 073991 atm ft3 R lbm 073023 atm cm3 Rg45586 Pa m3 Kkg83143 Pa m3 Kg83143 kPa m3 Kkg83143 kPa cm3. Gas constant R 8314459848 Jmol 1 K 1. The R gas constant is common for.
The digits inside the parentheses are the uncertainty in the measurement of gas constant value. Air gas constant is RairR289702869 Jg K2869 Jkg K Wiki User. This value is appropriate for air if Joule is chosen for the unit of energy kg as unit of mass and K as unit of temperature ie.
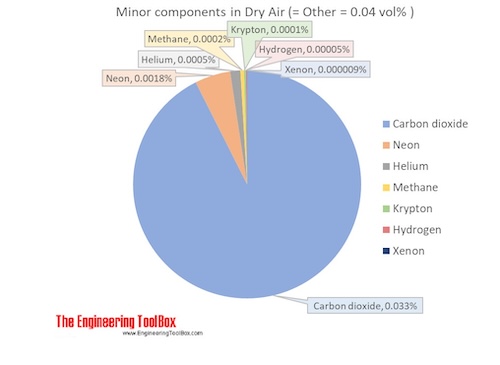
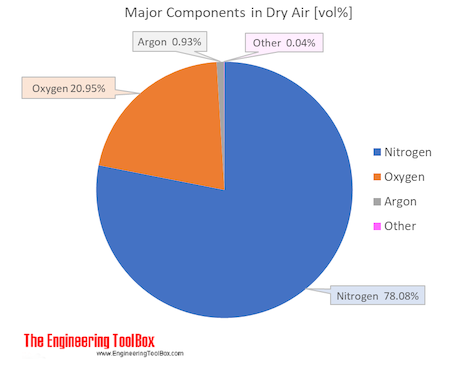
Heat transfer rate W m 2 8806 1 0 5 Btu ft 2 s. Air is a mixture of gases 78 nitrogen and 21 oxygen with traces of water vapor carbon dioxide argon and various other components. Temperature in degrees Fahrenheit F.
R 8314510 Pa m3 K-1 mol-1 8314510 Pa L K-1 mol-1. The atomic weight of elemental nitrogen for example in English units is A rnitrogen 140067 lbmlbmol and the molecular weight of air is Universal gas constant and ideal gas law The universal gas constant R u is as its name implies universal ie. Any gas has certain properties that we can detect with our senses.
However the dedicated Gas Constant calculator in Uconeer calculates the value of R based on over 900. P Pressure bar atmosphere Pa V Gaseous volume m 3 cm 3 n number of gaseous moles dimensionless R Universal gas constant JmolK litatmmolK T Temperature of the gas K 0 C R is also known by alternative names such as Ideal gas constant molar gas constant or simply R gas constant. Some gas constant value in different units are listed below-.
Gas Constant In Different Units. The Gas Constant R from the Ideal Gas Law is 8314462 Joules moles Kelvin. R 10731573ft³psiaRlbmol 073024026ft³atmRlbmol 820573383cm³atmKgmol 00831446LbarKgmol 83144598m³PaKgmol.
The ideal gas law in terms of R u is. The gas constant has the same unit as of entropy and molar heat capacity. Temperature in degrees Rankine R.
The value of the gas constant in SI unit is 8314 J mol 1 K 1. In SI units the value of the gas constant R is. The molecular weight of elemental atomic nitrogen for example in English units is Mnitrogen 140067 lbmlbmol and the molecular weight of air is air lbm 2897 lbmol M.


Comments
Post a Comment